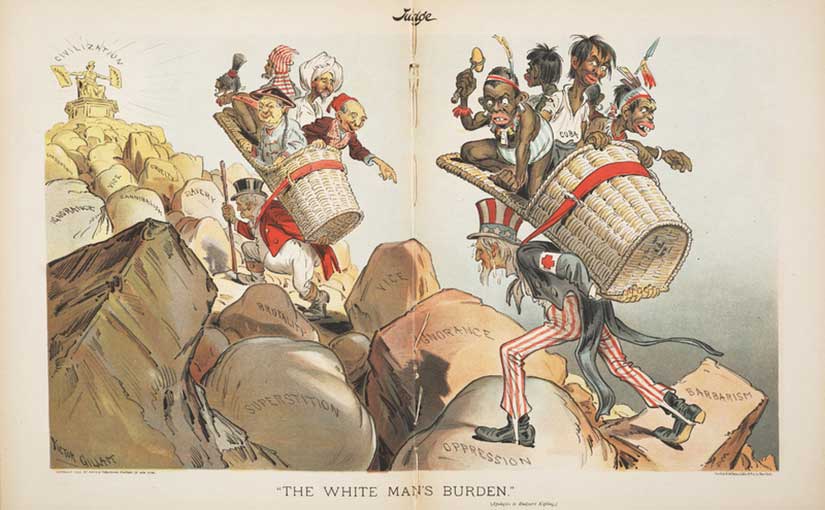
Georgie looked over at the weapon Pedro still held in his hand, and she shivered. No matter how she felt about Rosa, she could not send her away with this man.
She had to figure out a way to scare Pedro off. “The Insulares will come. Soldados!”
Filipinos had been put to death for far less than waving a knife in the face of an American. What good was the Insular bogeyman if she didn’t let him out of the closet once in a while?
The Insular bogeyman? Is this some strange Grimm’s fairy tale you haven’t heard of? Oh, no, it is something far more insidious: it’s a euphemism, a legal one.
Euphemisms were a whole new tongue spoken in nineteenth-century America. In fact, I should not even say “tongue” because it could give you all sorts of salacious ideas. English naval captain Edward Marryat got in trouble for asking a female companion if she had hurt her leg when she had tripped, and he was informed that proper Americans did not use that word (leg). “Limb” was specific enough, thank you very much.
So, if you cannot say leg, you probably cannot say colony. No, the word colony does not have sexual undertones—at least, not that I know of—but it is still a troubling word for a formerly rebellious colony founded upon Enlightenment ideals of self-determination and personal liberty. What, the United States an empire?
Even Thomas Jefferson admitted it was—though he called it an “empire of liberty” that would expand westward and check the growth of the British menace, beginning with the 1803 purchase of Louisiana from the French. Jefferson wrote to James Madison: “I am persuaded no constitution was ever before so well calculated as ours for extensive empire and self-government.” He saw no irony in defending, in the same breath, the right of self-government alongside the right to empire. In fact, he (like many today) believed that America’s democratic history, transparent legal system, and free market economy made it especially suited to transform the world for good and fight barbarism: American exceptionalism.
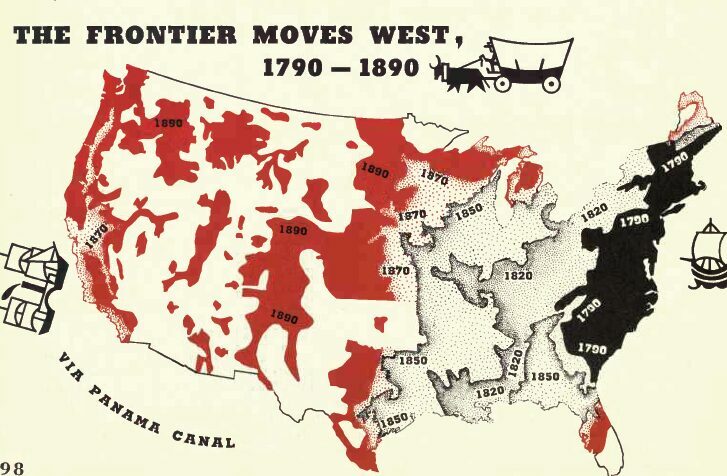
In the resulting growth of (mostly white) settlements across the North American continent, the word “empire” was avoided. These were “territories” along America’s “frontier”—territories on their way to statehood, a distinction that was not granted to later acquisitions. According to Frederick Jackson Turner, the frontier helped preserve liberty and egalitarianism through free access to land (by taking it from Indigenous Americans) and preventing a landed aristocracy from developing (Gilded Age, anyone?). Out on the frontier, any (white) man could make something of himself, as long as he survived.
(If none of this sounds truly democratic, you’re right. You’re not the first modern reader to notice, trust me. As even Mark Twain wrote in 1901: “The Blessings of Civilization are all right, and a good commercial property; there could not be a better, in a dim light.” [Emphasis mine.] Don’t look too closely, in other words.)
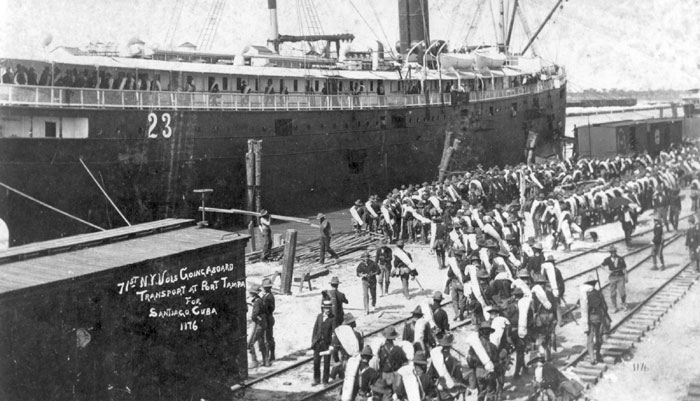
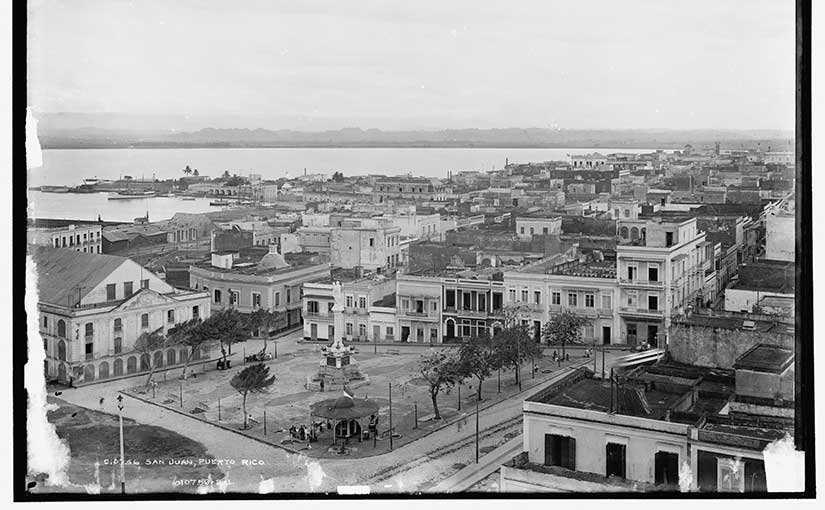
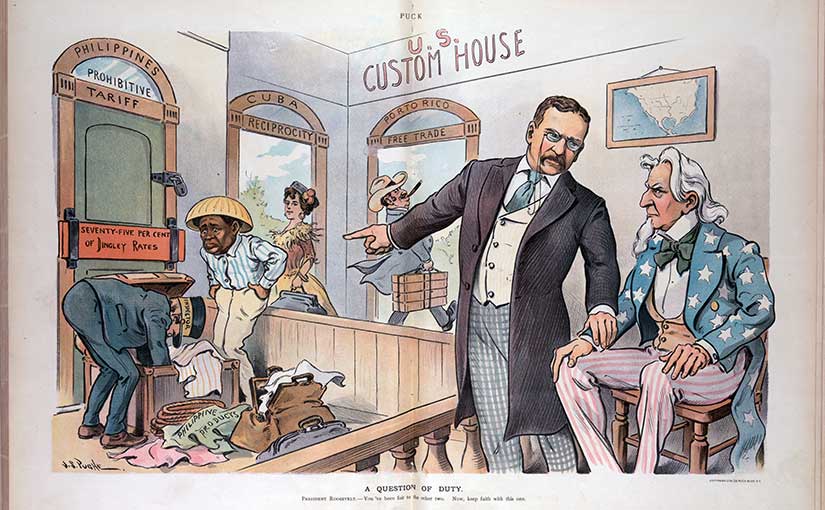
Back to our discussion of “territories.” In the Treaty of Paris ending the Spanish-American War in December 1898, the United States purchased the Philippines, Puerto Rico, and Guam from Spain. While the western frontier had expanded slowly enough to look like natural growth, this acquisition came in one fell swoop. What makes a piece of land a colony for Spain and not a colony when purchased from Spain by America? Good question.

Imperialists wanted a new word: insular. Geographer Scott Kirsch commented that the choice insular reflected “novel anxieties over America’s new place at the seat of an interconnected global empire.” It fit for three reasons:
First, these new possessions were islands, and the primary definition of insular is “of or pertaining to islands.” What a great way to differentiate the Philippines, Puerto Rico, and Guam from the continental territories. Interestingly, though, Hawaii will not become an insular territory, despite being a cluster of islands. Instead, in the midst of the Spanish-American War, Hawaii had been enthusiastically annexed by Congress, an about-face since the country had rejected that opportunity only five years previously. A lot had happened in those five years, as you can read here. And if Hawaii didn’t count as insular, there had to be more to the word than just geography.
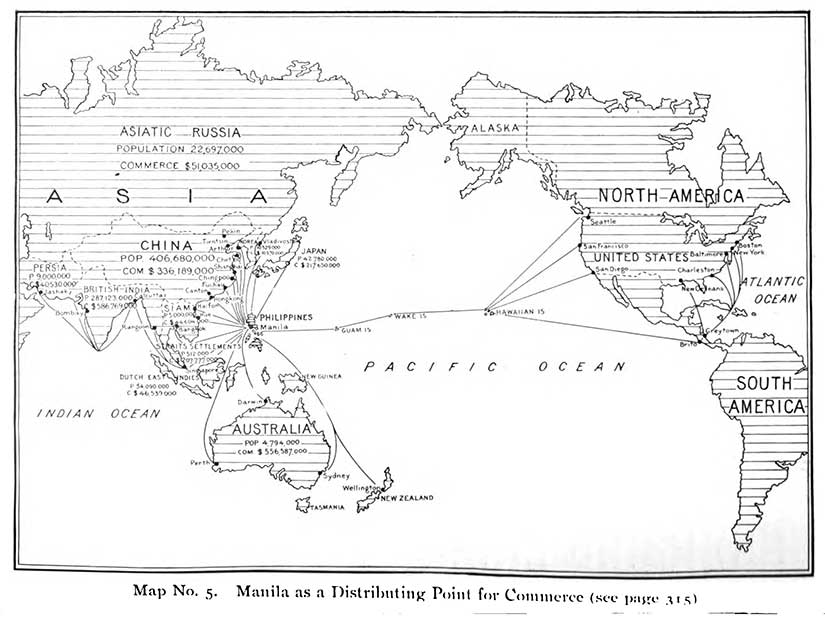
A second meaning of insular is “Detached or standing out by itself like an island; insulated.” This is where the word becomes perfect for how America wants to see its new acquisitions, particularly as relates to the Philippines. In the “scramble for the Pacific,” America had found itself left out of China. Secretary of State John Hay would address this particular issue in the Open Door memos, asserting the right of all nations to trade freely and equally in China. But the truth was that the US did not want to get too involved in China. It wanted the benefit of a Pacific entrepôt without being too Sinified.
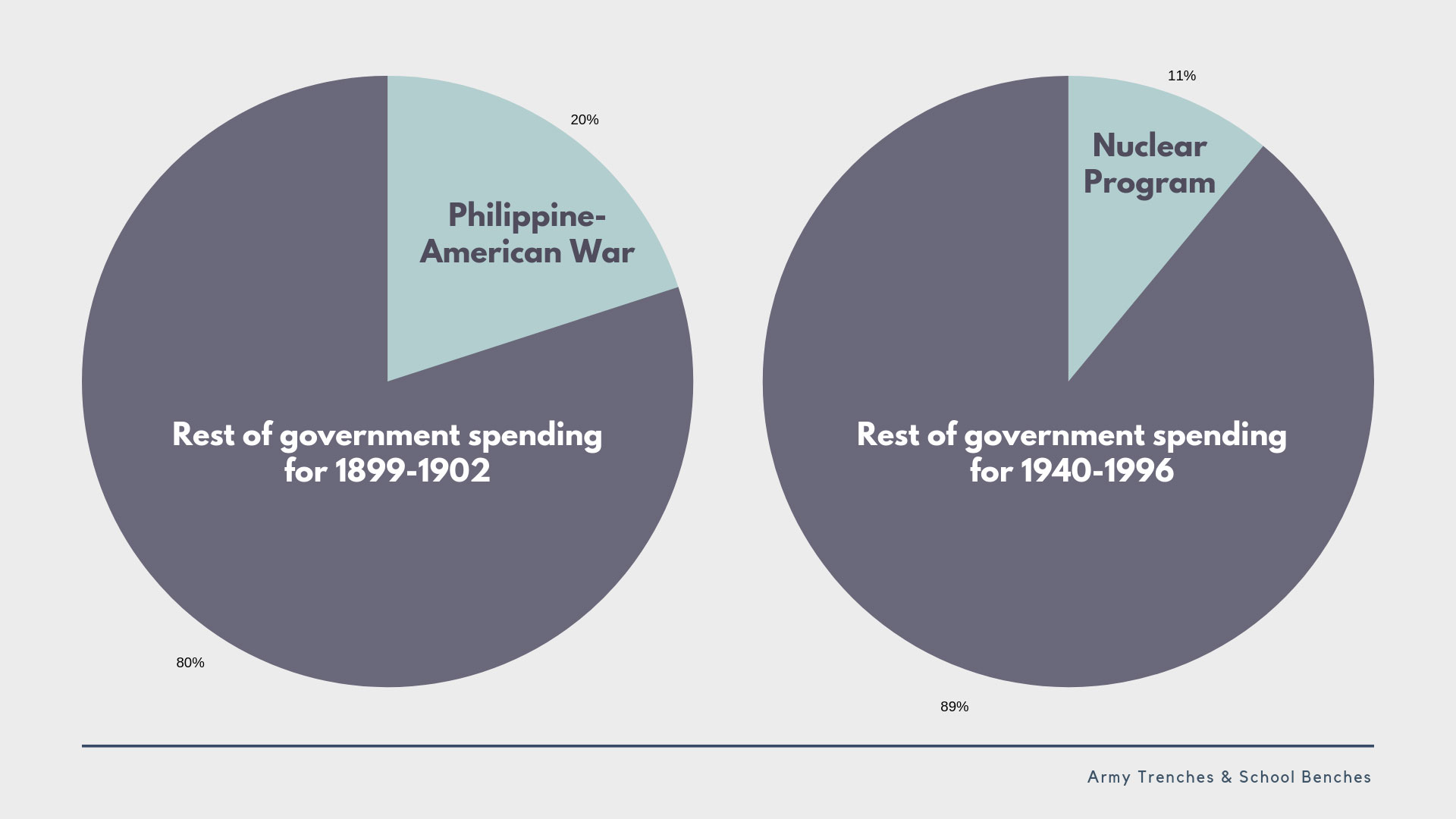
Manila had been the Spanish answer to cashing in on China while simultaneously insulating themselves from China, and the Americans thought it a brilliant idea. In a 1902 National Geographic article by the Honorable O. P. Austin, the Chief of the Bureau of Statistics of the Treasury Department, Manila would become the channel through which all of this wealth would pass, an off-shore customs and clearinghouse for goods bound for the United States. With the 1902 extension of the Chinese Exclusion Act—extended now to exclude Chinese from the Philippines, too—our new insular possessions would not be a conduit for people, just money. According to Scott Kirsch, this “coupled the virtues of proximity to Asia with a distinctive sense of separation from it.”
Because, really, America wanted to be insulated from their own empire. This is the third reason the term insular fits so well. The definition of a colony is “a body of people who settle in a new locality, forming a community subject to or connected with their parent state.” This implies spreading both people and ideas to the new lands. Americans were willing to do the latter. In fact, President William McKinley asserted the idea of “benevolent assimilation”—that “we come not as invaders or conquerors, but as friends, to protect the natives in their homes, in their employments, and in their personal and religious rights.” Americans spread their language, their pedagogical ideals (see posts on Thomasites and pensionados), their sanitation principles, their political administration, and their products (Spam, anyone?) to the Philippines with gusto.
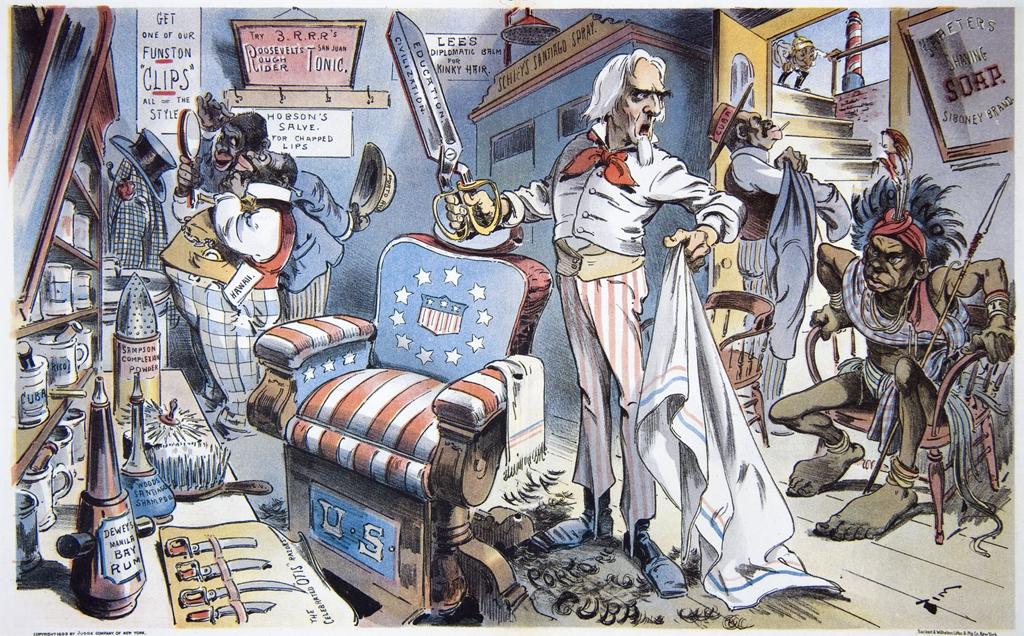
But most Americans did not intend to settle in the Philippines permanently, which meant that it was not a colony in the true sense of the word. They meant to fashion Filipinos as Americans and leave, hence the emphasis on shaping the educational system with an eye toward self-replication. Even anti-imperialists like William Jennings Bryan, the failed 1900 Democratic candidate for president, felt this way. He wanted to close the door to Asian immigration, and during the debate about Chinese exclusion, he wrote:
“Let us educate the Chinese who desire to learn of American institutions; let us offer courtesy and protection to those who come here to travel and investigate, but it will not be of permanent benefit to either the Chinese or to us to invite them to become citizens or to permit them to labor here and carry the proceeds of their toil back to their own country.”
He felt the same about the Japanese and all other Asian races. His article is a defense of exclusion and intolerance: “It is not necessary nor even wise that the family environment should be broken up or that all who desire entrance should be admitted to the family circle. In a larger sense a nation is a family.” Bryan’s English and Irish ancestors had immigrated two hundred years earlier, so you can pardon him for forgetting that he was an immigrant, too. But he was typical in wanting to turn off the tap, and a colony would not have permitted that insularity as easily.

This was not just about race, though. Americans wanted the Philippines to remain politically and economically separate. Eventually, one had to ask as the United States grew bigger: does the Constitution follow the flag? If the people of the Philippines, Puerto Rico, and Guam are living under American government, should they have the rights of American citizens? A longer treatment of this topic is handled here, but the short answer for the Philippines was no. The Insular Cases in the United States Supreme Court maintained that the Philippines was an unincorporated territory, and while its citizens had natural rights, such as religion and property, they did not have full political rights, nor citizenship. This was an easier line to skirt when the government ruling the Philippines was part of the Bureau of Insular Affairs in the War Department, not a Colonial Office. Labels do matter.
And strangely William Jennings Bryan, no friend of the Asian immigrant in general, actually pointed out the inconsistency of Americans flooding the Philippines while not allowing the same in return:
“If…the Filipinos are prohibited from coming here (if a republic can prohibit the inhabitants of one part from visiting another part of the republic), will it not excite a just protest on the part of the Filipinos? How can we excuse ourselves if we insist upon opening the Philippine islands to the invasion of American capital, American speculators, and American task-masters, and yet close our doors to those Filipinos who, driven from home, may seek an asylum here?”
Bryan’s solution was immediate independence for the Philippines, but the Supreme Court had a different solution: the Philippines, Puerto Rico, and Guam were not a part of our republic. Insular was not inside. The justices bent over backward to draw the distinction that Americans wanted, even if they essentially made up law to do it. Since both imperialists and anti-imperialists both agreed, in the words of Andrew Carnegie, that “Americans cannot be grown [in the Philippines],” no one complained that the court had exceeded its mandate. The insular designation stuck.
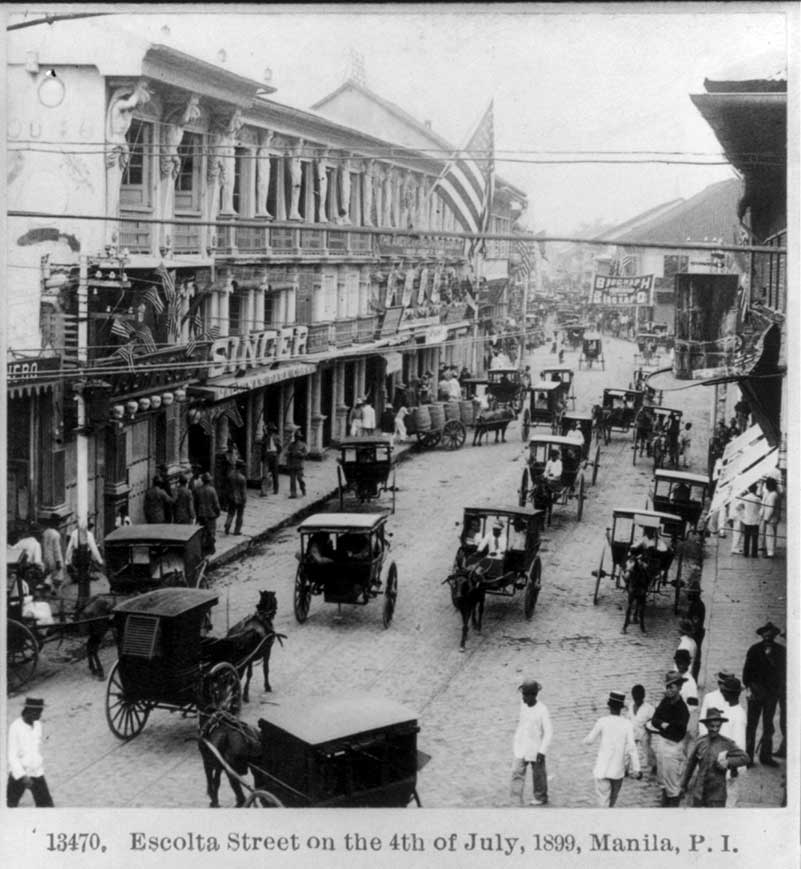

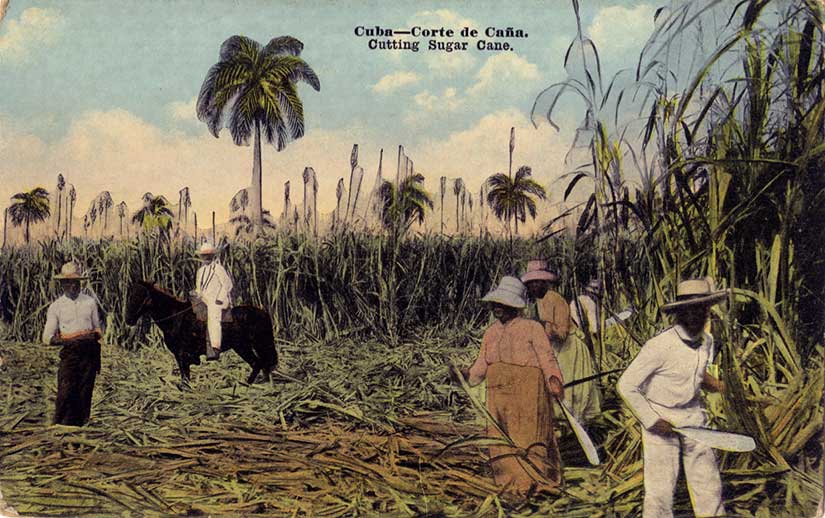
Another benefit of insular territories was that free trade need not be extended right away—especially if there were concerns that the islands might compete too well in certain key industries, like sugar and tobacco. It was favorable for American producers to keep them out. While American goods could enter the Philippines freely—because Americans in the Insular Government set Philippine trade policy—Filipino goods were taxed both leaving the Philippines and entering the United States because the U.S. Congress set American trade policy. That was the beauty of the insular cases.
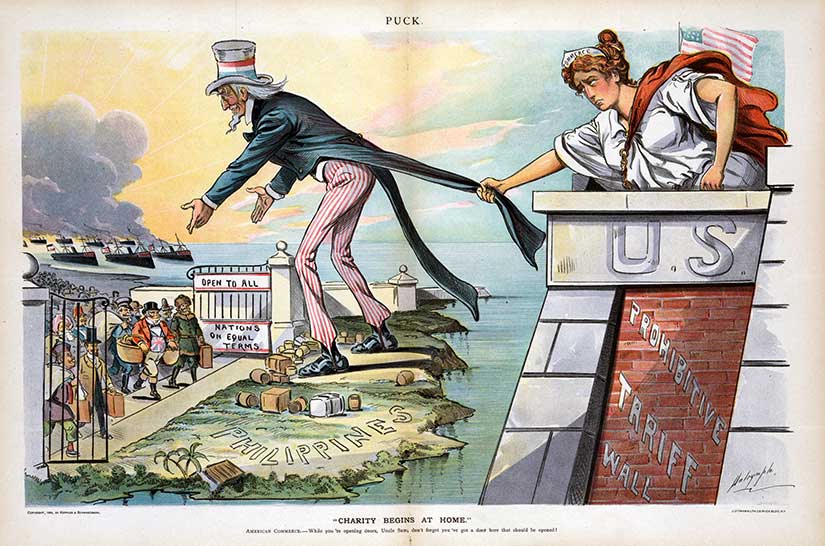
When I teach my course on America in the Philippines, students who have at least read the course description know that the United States had its own empire—but surprisingly few adults do. They might know about Guam or Puerto Rico, and they might even call these “territories,” but if you ask them the difference between a colony and a territory, they do not have a good answer. And I do not blame them because America’s “insular” language has left its citizens deliberately insulated from clarity.
I do not think Filipinos are confused, though. They easily call the years between 1898 and 1934 the American Colonial Period, and many would also include the 1934 to 1946 Commonwealth Period (not counting the Japanese occupation of 1941-1945).
Unfortunately, if we Americans do not take a hard look at our history, we are doomed to repeat our mistakes and therefore reinforce the (mis)perceptions others have of us. One of my goals in writing the Sugar Sun series was to bring this history to a general public—along with some sex, drugs, and violence to really sell it. I love romance, so it was my medium of choice, but the Philippine setting, diverse characters, and political undertones are all part of my historical mission.
The Person Sitting in Darkness is almost sure to say: “There is something curious about this–curious and unaccountable. There must be two Americas: one that sets the captive free, and one that takes a once-captive’s new freedom away from him, and picks a quarrel with him with nothing to found it on; then kills him to get his land.”
— Mark Twain, “To the Person Sitting in Darkness,” 1901
Featured image of “The man behind the gun will settle this war,” from Puck.